Implement the BSTIterator class that represents an iterator over the in-order traversal of a binary search tree (BST):
-
BSTIterator(TreeNode root)Initializes an object of theBSTIteratorclass. Therootof the BST is given as part of the constructor. The pointer should be initialized to a non-existent number smaller than any element in the BST. -
boolean hasNext()Returnstrueif there exists a number in the traversal to the right of the pointer, otherwise returnsfalse. -
int next()Moves the pointer to the right, then returns the number at the pointer. Notice that by initializing the pointer to a non-existent smallest number, the first call tonext()will return the smallest element in the BST. You may assume thatnext()calls will always be valid. That is, there will be at least a next number in the in-order traversal whennext()is called.
Test Cases
Example 1:
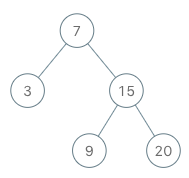
**Input**
["BSTIterator", "next", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext"]
[[[7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], []]
**Output**
[null, 3, 7, true, 9, true, 15, true, 20, false]
**Explanation**
BSTIterator bSTIterator = new BSTIterator([7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]);
bSTIterator.next(); // return 3
bSTIterator.next(); // return 7
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return True
bSTIterator.next(); // return 9
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return True
bSTIterator.next(); // return 15
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return True
bSTIterator.next(); // return 20
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return False
Constraints:
-
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 10<sup>5</sup>]. -
0 <= Node.val <= 10<sup>6</sup> -
At most
10<sup>5</sup>calls will be made tohasNext, andnext.
Follow up:
- Could you implement
next()andhasNext()to run in averageO(1)time and useO(h)memory, wherehis the height of the tree?
Solution
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class BSTIterator {
queue<int> q;
void inOrder(TreeNode* root, queue<int> &q) {
if(root == NULL){
return;
}
inOrder(root->left, q);
q.push(root->val);
inOrder(root->right, q);
}
public:
BSTIterator(TreeNode* root) {
inOrder(root, q);
}
int next() {
if(!q.empty()){
int frontNode = q.front();
q.pop();
return frontNode;
}
return 0;
}
bool hasNext() {
if(!q.empty()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
/**
* Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* BSTIterator* obj = new BSTIterator(root);
* int param_1 = obj->next();
* bool param_2 = obj->hasNext();
*//**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class BSTIterator {
private Deque<TreeNode> stack;
public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) {
stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
TreeNode next = root;
while(next != null) {
stack.offerLast(next);
next = next.left;
}
}
public int next() {
TreeNode removedNode = stack.pollLast();
TreeNode next = removedNode.right;
while(next != null) {
stack.offerLast(next);
next = next.left;
}
return removedNode.val;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return !stack.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* BSTIterator obj = new BSTIterator(root);
* int param_1 = obj.next();
* boolean param_2 = obj.hasNext();
*/# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class BSTIterator:
def __init__(self, root: TreeNode):
self.lst = []
self.index = 0
if root:
st = [root]
while len(st) > 0:
x = st.pop()
self.lst.append(x.val)
if x.left: st.append(x.left)
if x.right: st.append(x.right)
self.lst = sorted(self.lst)
print(self.lst)
def next(self) -> int:
"""
@return the next smallest number
"""
x = self.lst[self.index]
self.index += 1
return x
def hasNext(self) -> bool:
"""
@return whether we have a next smallest number
"""
if len(self.lst) == 0: return False
if self.index < len(self.lst):
return True
return False
# Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = BSTIterator(root)
# param_1 = obj.next()
# param_2 = obj.hasNext()