You are given a perfect binary tree where all leaves are on the same level, and every parent has two children. The binary tree has the following definition:
class Node {
int val;
Node left;
Node right;
Node next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
How to Solve
To solve, we will be traversing the tree per level.
For each node curr on a particular level (would already have next pointer due to parent level), do following
- if
curr.leftis not null, point its next tocurr.right - if
curr.rightis not null, point its next tocurrneighbouring child curr = curr.next
For next level, move to level.left
Test Cases
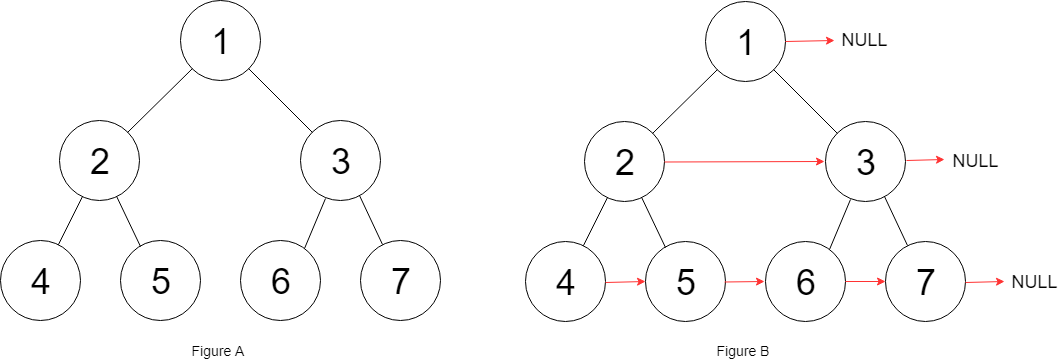
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [1,#,2,3,#,4,5,6,7,#]
Explanation: Given the above perfect binary tree (Figure A),
your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B.
The serialized output is in level order as connected by the next pointers,
with '#' signifying the end of each level.
Example 2:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Solution
package populating_next_right_pointers_in_each_node
type Node struct {
Val int
Left *Node
Right *Node
Next *Node
}
func connect(root *Node) *Node {
level := root
for level != nil {
curr := level
for curr != nil {
if curr.Left != nil {
curr.Left.Next = curr.Right
}
if curr.Right != nil && curr.Next != nil {
curr.Right.Next = curr.Next.Left
}
curr = curr.Next
}
level = level.Left
}
return root
}class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node next;
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
};
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
Node level=root;
while(level!=null){
Node cur=level;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.left!=null) cur.left.next=cur.right;
if(cur.right!=null && cur.next!=null) cur.right.next=cur.next.left;
cur=cur.next;
}
level=level.left;
}
return root;
}
}class Node:
def __init__(self, val: int = 0, left: 'Node' = None, right: 'Node' = None, next: 'Node' = None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
self.next = next
class Solution:
def connect(self, root: 'Optional[Node]') -> 'Optional[Node]':
level = root
while level is not None:
curr = level
while curr is not None:
if curr.left is not None:
curr.left.next = curr.right
if curr.right is not None and curr.next is not None:
curr.right.next = curr.next.left
curr = curr.next
level = level.left
return root