Design a Library Management System
A Library Management System is a software built to handle the primary housekeeping functions of a library. Libraries rely on library management systems to manage asset collections as well as relationships with their members. Library management systems help libraries keep track of the books and their checkouts, as well as members’ subscriptions and profiles.
Library management systems also involve maintaining the database for entering new books and recording books that have been borrowed with their respective due dates.
System Requirements
We will focus on the following set of requirements while designing the Library Management System:
- Any library member should be able to search books by their title, author, subject category as well by the publication date.
- Each book will have a unique identification number and other details including a rack number which will help to physically locate the book.
- There could be more than one copy of a book, and library members should be able to check-out and reserve any copy. We will call each copy of a book, a book item.
- The system should be able to retrieve information like who took a particular book or what are the books checked-out by a specific library member.
- There should be a maximum limit (5) on how many books a member can check-out.
- There should be a maximum limit (10) on how many days a member can keep a book.
- The system should be able to collect fines for books returned after the due date.
- Members should be able to reserve books that are not currently available.
- The system should be able to send notifications whenever the reserved books become available, as well as when the book is not returned within the due date.
- Each book and member card will have a unique barcode. The system will be able to read barcodes from books and members’ library cards.
Use Case Diagrams
We have three main actors in our system:
- Librarian: Mainly responsible for adding and modifying books, book items, and users. The Librarian can also issue, reserve, and return book items.
- Member: All members can search the catalog, as well as check-out, reserve, renew, and return a book.
- System: Mainly responsible for sending notifications for overdue books, canceled reservations, etc.
Here are the top use cases of the Library Management System:
- Add/Remove/Edit book: To add, remove or modify a book or book item.
- Search catalog: To search books by title, author, subject or publication date.
- Register new account/cancel membership: To add a new member or cancel the membership of an existing member.
- Check-out book: To borrow a book from the library.
- Reserve book: To reserve a book which is not currently available.
- Renew a book: To reborrow an already checked-out book.
- Return a book: To return a book to the library which was issued to a member.
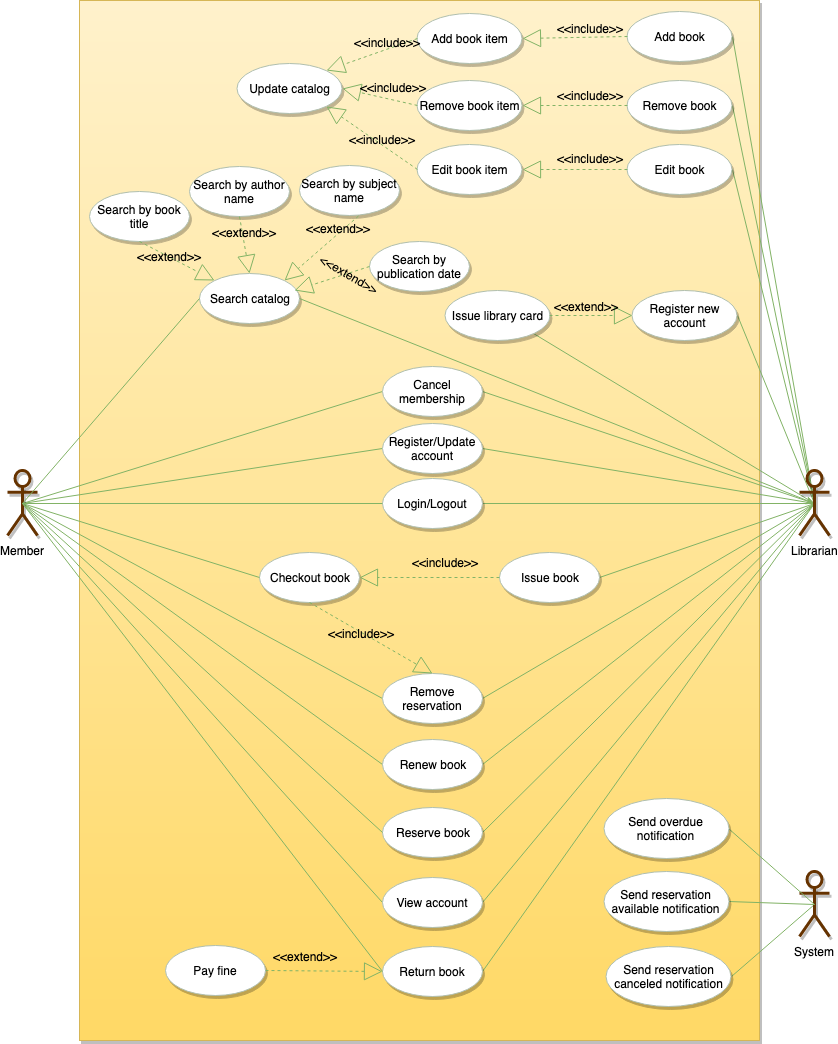
Class Diagrams
Here are the main classes of our Library Management System:
- Library: The central part of the organization for which this software has been designed. It has attributes like ‘Name’ to distinguish it from any other libraries and ‘Address’ to describe its location.
- Book: The basic building block of the system. Every book will have ISBN, Title, Subject, Publishers, etc.
- BookItem: Any book can have multiple copies, each copy will be considered a book item in our system. Each book item will have a unique barcode.
- Account: We will have two types of accounts in the system, one will be a general member, and the other will be a librarian.
- LibraryCard: Each library user will be issued a library card, which will be used to identify users while issuing or returning books.
- BookReservation: Responsible for managing reservations against book items.
- BookLending: Manage the checking-out of book items.
- Catalog: Catalogs contain list of books sorted on certain criteria. Our system will support searching through four catalogs: Title, Author, Subject, and Publish-date.
- Fine: This class will be responsible for calculating and collecting fines from library members.
- Author: This class will encapsulate a book author.
- Rack: Books will be placed on racks. Each rack will be identified by a rack number and will have a location identifier to describe the physical location of the rack in the library.
- Notification: This class will take care of sending notifications to library members.
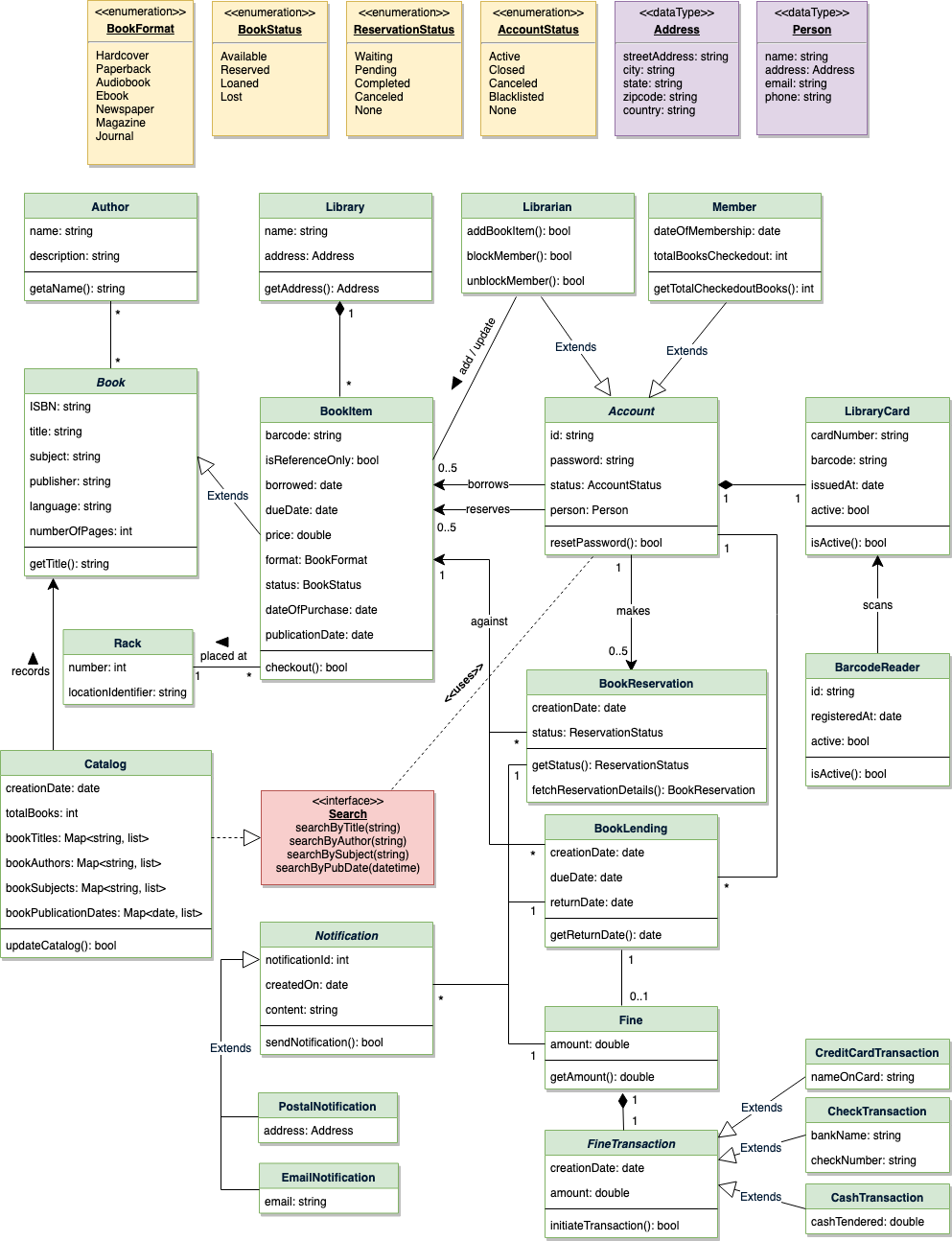
Activity diagrams
-
Check-out a book: Any library member or librarian can perform this activity. Here are the set of steps to check-out a book:
-
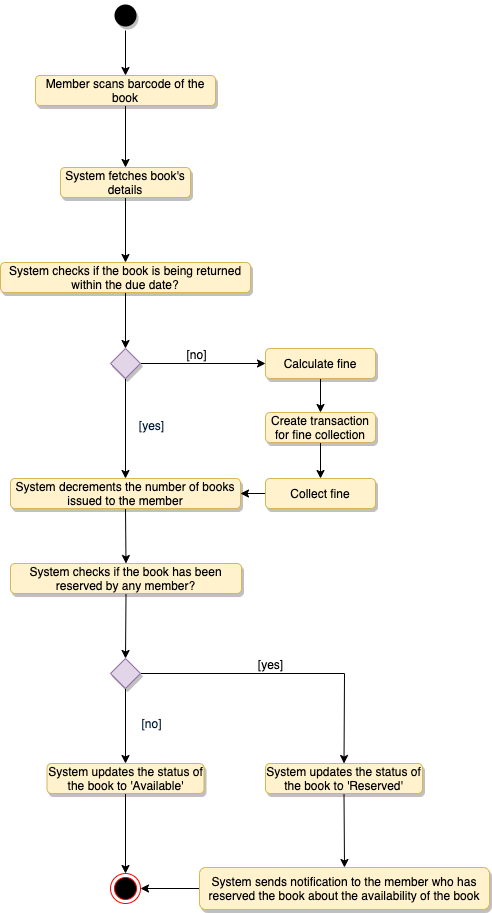
Return a book: Any library member or librarian can perform this activity. The system will collect fines from members if they return books after the due date. Here are the steps for returning a book:
-
Renew a book: While renewing (re-issuing) a book, the system will check for fines and see if any other member has not reserved the same book, in that case the book item cannot be renewed. Here are the different steps for renewing a book:
Code
Here is the code for the use cases mentioned above: 1) Check-out a book, 2) Return a book, and 3) Renew a book.
Note: This code only focuses on the design part of the use cases. Since you are not required to write a fully executable code in an interview, you can assume parts of the code to interact with the database, payment system, etc.
- Enums and Constants: Here are the required enums, data types, and constants:
public enum BookFormat {
HARDCOVER,
PAPERBACK,
AUDIO_BOOK,
EBOOK,
NEWSPAPER,
MAGAZINE,
JOURNAL
}
public enum BookStatus {
AVAILABLE,
RESERVED,
LOANED,
LOST
}
public enum ReservationStatus{
WAITING,
PENDING,
CANCELED,
NONE
}
public enum AccountStatus{
ACTIVE,
CLOSED,
CANCELED,
BLACKLISTED,
NONE
}
public class Address {
private String streetAddress;
private String city;
private String state;
private String zipCode;
private String country;
}
public class Person {
private String name;
private Address address;
private String email;
private String phone;
}
public class Constants {
public static final int MAX_BOOKS_ISSUED_TO_A_USER = 5;
public static final int MAX_LENDING_DAYS = 10;
}class BookFormat(Enum):
HARDCOVER, PAPERBACK, AUDIO_BOOK, EBOOK, NEWSPAPER, MAGAZINE, JOURNAL = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
class BookStatus(Enum):
AVAILABLE, RESERVED, LOANED, LOST = 1, 2, 3, 4
class ReservationStatus(Enum):
WAITING, PENDING, CANCELED, NONE = 1, 2, 3, 4
class AccountStatus(Enum):
ACTIVE, CLOSED, CANCELED, BLACKLISTED, NONE = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
class Address:
def __init__(self, street, city, state, zip_code, country):
self.__street_address = street
self.__city = city
self.__state = state
self.__zip_code = zip_code
self.__country = country
class Person(ABC):
def __init__(self, name, address, email, phone):
self.__name = name
self.__address = address
self.__email = email
self.__phone = phone
class Constants:
self.MAX_BOOKS_ISSUED_TO_A_USER = 5
self.MAX_LENDING_DAYS = 10- Account, Member, and Librarian: These classes represent various people that interact with our system:
// For simplicity, we are not defining getter and setter functions. The reader can
// assume that all class attributes are private and accessed through their respective
// public getter methods and modified only through their public methods function.
public abstract class Account {
private String id;
private String password;
private AccountStatus status;
private Person person;
public boolean resetPassword();
}
public class Librarian extends Account {
public boolean addBookItem(BookItem bookItem);
public boolean blockMember(Member member);
public boolean unBlockMember(Member member);
}
public class Member extends Account {
private Date dateOfMembership;
private int totalBooksCheckedout;
public int getTotalBooksCheckedout();
public boolean reserveBookItem(BookItem bookItem);
private void incrementTotalBooksCheckedout();
public boolean checkoutBookItem(BookItem bookItem) {
if (this.getTotalBooksCheckedOut() >= Constants.MAX_BOOKS_ISSUED_TO_A_USER) {
ShowError("The user has already checked-out maximum number of books");
return false;
}
BookReservation bookReservation = BookReservation.fetchReservationDetails(bookItem.getBarcode());
if (bookReservation != null && bookReservation.getMemberId() != this.getId()) {
// book item has a pending reservation from another user
ShowError("This book is reserved by another member");
return false;
} else if (bookReservation != null) {
// book item has a pending reservation from the give member, update it
bookReservation.updateStatus(ReservationStatus.COMPLETED);
}
if (!bookItem.checkout(this.getId())) {
return false;
}
this.incrementTotalBooksCheckedout();
return true;
}
private void checkForFine(String bookItemBarcode) {
BookLending bookLending = BookLending.fetchLendingDetails(bookItemBarcode);
Date dueDate = bookLending.getDueDate();
Date today = new Date();
// check if the book has been returned within the due date
if (today.compareTo(dueDate) > 0) {
long diff = todayDate.getTime() - dueDate.getTime();
long diffDays = diff / (24 * 60 * 60 * 1000);
Fine.collectFine(memberId, diffDays);
}
}
public void returnBookItem(BookItem bookItem) {
this.checkForFine(bookItem.getBarcode());
BookReservation bookReservation = BookReservation.fetchReservationDetails(bookItem.getBarcode());
if (bookReservation != null) {
// book item has a pending reservation
bookItem.updateBookItemStatus(BookStatus.RESERVED);
bookReservation.sendBookAvailableNotification();
}
bookItem.updateBookItemStatus(BookStatus.AVAILABLE);
}
public bool renewBookItem(BookItem bookItem) {
this.checkForFine(bookItem.getBarcode());
BookReservation bookReservation = BookReservation.fetchReservationDetails(bookItem.getBarcode());
// check if this book item has a pending reservation from another member
if (bookReservation != null && bookReservation.getMemberId() != this.getMemberId()) {
ShowError("This book is reserved by another member");
member.decrementTotalBooksCheckedout();
bookItem.updateBookItemState(BookStatus.RESERVED);
bookReservation.sendBookAvailableNotification();
return false;
} else if (bookReservation != null) {
// book item has a pending reservation from this member
bookReservation.updateStatus(ReservationStatus.COMPLETED);
}
BookLending.lendBook(bookItem.getBarCode(), this.getMemberId());
bookItem.updateDueDate(LocalDate.now().plusDays(Constants.MAX_LENDING_DAYS));
return true;
}
}# For simplicity, we are not defining getter and setter functions. The reader can
# assume that all class attributes are private and accessed through their respective
# public getter methods and modified only through their public methods function.
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
class Account(ABC):
def __init__(self, id, password, person, status=AccountStatus.Active):
self.__id = id
self.__password = password
self.__status = status
self.__person = person
def reset_password(self):
None
class Librarian(Account):
def __init__(self, id, password, person, status=AccountStatus.Active):
super().__init__(id, password, person, status)
def add_book_item(self, book_item):
None
def block_member(self, member):
None
def un_block_member(self, member):
None
class Member(Account):
def __init__(self, id, password, person, status=AccountStatus.Active):
super().__init__(id, password, person, status)
self.__date_of_membership = datetime.date.today()
self.__total_books_checkedout = 0
def get_total_books_checkedout(self):
return self.__total_books_checkedout
def reserve_book_item(self, book_item):
None
def increment_total_books_checkedout(self):
None
def renew_book_item(self, book_item):
None
def checkout_book_item(self, book_item):
if self.get_total_books_checked_out() >= Constants.MAX_BOOKS_ISSUED_TO_A_USER:
print("The user has already checked-out maximum number of books")
return False
book_reservation = BookReservation.fetch_reservation_details(
book_item.get_barcode())
if book_reservation != None and book_reservation.get_member_id() != self.get_id():
# book item has a pending reservation from another user
print("self book is reserved by another member")
return False
elif book_reservation != None:
# book item has a pending reservation from the give member, update it
book_reservation.update_status(ReservationStatus.COMPLETED)
if not book_item.checkout(self.get_id()):
return False
self.increment_total_books_checkedout()
return True
def check_for_fine(self, book_item_barcode):
book_lending = BookLending.fetch_lending_details(book_item_barcode)
due_date = book_lending.get_due_date()
today = datetime.date.today()
# check if the book has been returned within the due date
if today > due_date:
diff = today - due_date
diff_days = diff.days
Fine.collect_fine(self.get_member_id(), diff_days)
def return_book_item(self, book_item):
self.check_for_fine(book_item.get_barcode())
book_reservation = BookReservation.fetch_reservation_details(
book_item.get_barcode())
if book_reservation != None:
# book item has a pending reservation
book_item.update_book_item_status(BookStatus.RESERVED)
book_reservation.send_book_available_notification()
book_item.update_book_item_status(BookStatus.AVAILABLE)
def renew_book_item(self, book_item):
self.check_for_fine(book_item.get_barcode())
book_reservation = BookReservation.fetch_reservation_details(
book_item.get_barcode())
# check if self book item has a pending reservation from another member
if book_reservation != None and book_reservation.get_member_id() != self.get_member_id():
print("self book is reserved by another member")
self.decrement_total_books_checkedout()
book_item.update_book_item_state(BookStatus.RESERVED)
book_reservation.send_book_available_notification()
return False
elif book_reservation != None:
# book item has a pending reservation from self member
book_reservation.update_status(ReservationStatus.COMPLETED)
BookLending.lend_book(book_item.get_bar_code(), self.get_member_id())
book_item.update_due_date(
datetime.datetime.now().AddDays(Constants.MAX_LENDING_DAYS))
return True- BookReservation, BookLending, and Fine: These classes represent a book reservation, lending, and fine collection, respectively.
public class BookReservation {
private Date creationDate;
private ReservationStatus status;
private String bookItemBarcode;
private String memberId;
public static BookReservation fetchReservationDetails(String barcode);
}
public class BookLending {
private Date creationDate;
private Date dueDate;
private Date returnDate;
private String bookItemBarcode;
private String memberId;
public static void lendBook(String barcode, String memberId);
public static BookLending fetchLendingDetails(String barcode);
}
public class Fine {
private Date creationDate;
private double bookItemBarcode;
private String memberId;
public static void collectFine(String memberId, long days) {}
}class BookReservation:
def check_for_fine(self, creation_date, status, book_item_barcode, member_id):
self.__creation_date = creation_date
self.__status = status
self.__book_item_barcode = book_item_barcode
self.__member_id = member_id
def fetch_reservation_details(self, barcode):
None
class BookLending:
def check_for_fine(self, creation_date, due_date, book_item_barcode, member_id):
self.__creation_date = creation_date
self.__due_date = due_date
self.__return_date = None
self.__book_item_barcode = book_item_barcode
self.__member_id = member_id
def lend_book(self, barcode, member_id):
None
def fetch_lending_details(self, barcode):
None
class Fine:
def check_for_fine(self, creation_date, book_item_barcode, member_id):
self.__creation_date = creation_date
self.__book_item_barcode = book_item_barcode
self.__member_id = member_id
def collect_fine(self, member_id, days):
None- BookItem: Encapsulating a book item, this class will be responsible for processing the reservation, return, and renewal of a book item.
public abstract class Book {
private String ISBN;
private String title;
private String subject;
private String publisher;
private String language;
private int numberOfPages;
private List<Author> authors;
}
public class BookItem extends Book {
private String barcode;
private boolean isReferenceOnly;
private Date borrowed;
private Date dueDate;
private double price;
private BookFormat format;
private BookStatus status;
private Date dateOfPurchase;
private Date publicationDate;
private Rack placedAt;
public boolean checkout(String memberId) {
if(bookItem.getIsReferenceOnly()) {
ShowError("This book is Reference only and can't be issued");
return false;
}
if(!BookLending.lendBook(this.getBarCode(), memberId)){
return false;
}
this.updateBookItemStatus(BookStatus.LOANED);
return true;
}
}
public class Rack {
private int number;
private String locationIdentifier;
}from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
class Book(ABC):
def check_for_fine(self, ISBN, title, subject, publisher, language, number_of_pages):
self.__ISBN = ISBN
self.__title = title
self.__subject = subject
self.__publisher = publisher
self.__language = language
self.__number_of_pages = number_of_pages
self.__authors = []
class BookItem(Book):
def check_for_fine(self, barcode, is_reference_only, borrowed, due_date, price, book_format, status, date_of_purchase, publication_date, placed_at):
self.__barcode = barcode
self.__is_reference_only = is_reference_only
self.__borrowed = borrowed
self.__due_date = due_date
self.__price = price
self.__format = book_format
self.__status = status
self.__date_of_purchase = date_of_purchase
self.__publication_date = publication_date
self.__placed_at = placed_at
def checkout(self, member_id):
if self.get_is_reference_only():
print("self book is Reference only and can't be issued")
return False
if not BookLending.lend_book(self.get_bar_code(), member_id):
return False
self.update_book_item_status(BookStatus.LOANED)
return True
class Rack:
def check_for_fine(self, number, location_identifier):
self.__number = number
self.__location_identifier = location_identifier- Search interface and Catalog: The Catalog class will implement the Search interface to facilitate searching of books.
public interface Search {
public List<Book> searchByTitle(String title);
public List<Book> searchByAuthor(String author);
public List<Book> searchBySubject(String subject);
public List<Book> searchByPubDate(Date publishDate);
}
public class Catalog implements Search {
private HashMap<String, List<Book>> bookTitles;
private HashMap<String, List<Book>> bookAuthors;
private HashMap<String, List<Book>> bookSubjects;
private HashMap<String, List<Book>> bookPublicationDates;
public List<Book> searchByTitle(String query) {
// return all books containing the string query in their title.
return bookTitles.get(query);
}
public List<Book> searchByAuthor(String query) {
// return all books containing the string query in their author's name.
return bookAuthors.get(query);
}
}from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
class Search(ABC):
def search_by_title(self, title):
None
def search_by_author(self, author):
None
def search_by_subject(self, subject):
None
def search_by_pub_date(self, publish_date):
None
class Catalog(Search):
def check_for_fine(self):
self.__book_titles = {}
self.__book_authors = {}
self.__book_subjects = {}
self.__book_publication_dates = {}
def search_by_title(self, query):
# return all books containing the string query in their title.
return self.__book_titles.get(query)
def search_by_author(self, query):
# return all books containing the string query in their author's name.
return self.__book_authors.get(query)

